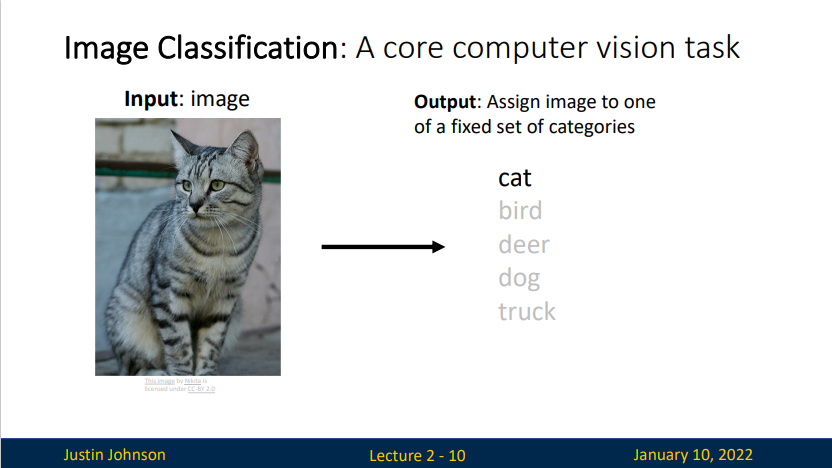
Image Classification
Concept
A core computer vision task
- Input: image.
- Output: Assign image to one of a fixed set of categories.
对于一个给定图像,程序要预测它属于哪一个类别(label)
Problem: Semantic Gap(语义鸿沟)
The semantic gap characterizes the difference between two descriptions of an object by different linguistic representations, for instance languages or symbols.
An image is a big grid of numbers between \([0,255]\)
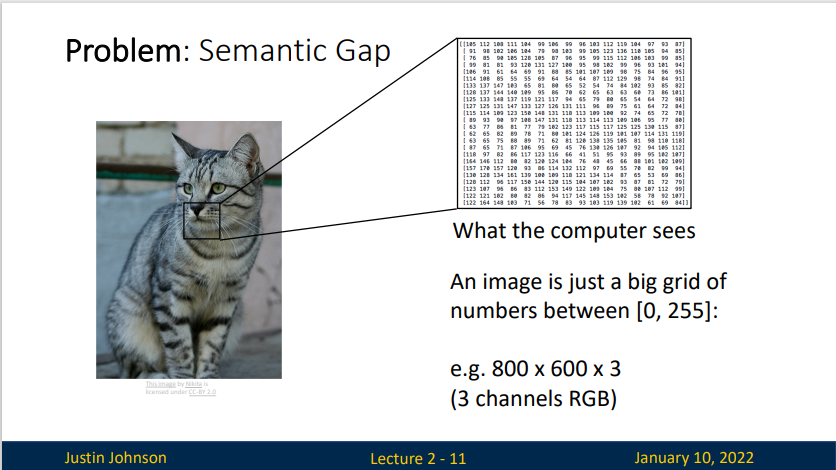
上图的图像宽600像素,高度800像素,有三个颜色通道(RGB)
也就是说,这个图像包含了\(600\times800\times3 =1440000\)个数字。我们的任务就是将这上百万的数字变成一个简单的标签。比如说,“猫”
Challenges:
- Viewpoint Variation 视觉变化 不同角度的猫猫
- Intraclass Variation 类内差异 狸花猫与三花猫
- Fine-Grained Categories 精细差异 Maine Coon 与 Ragdoll
- Background Clutter 背景干扰 融入背景的猫猫
- Illumination Changes 光照变化 不同光线的猫猫
- Deformation 形变 猫猫的变形
- Occlusion 遮挡 草丛中的猫猫
Image Classification
图像分类是计算机视觉的基础,用来构建更多更复杂的应用程序,比如说目标检测
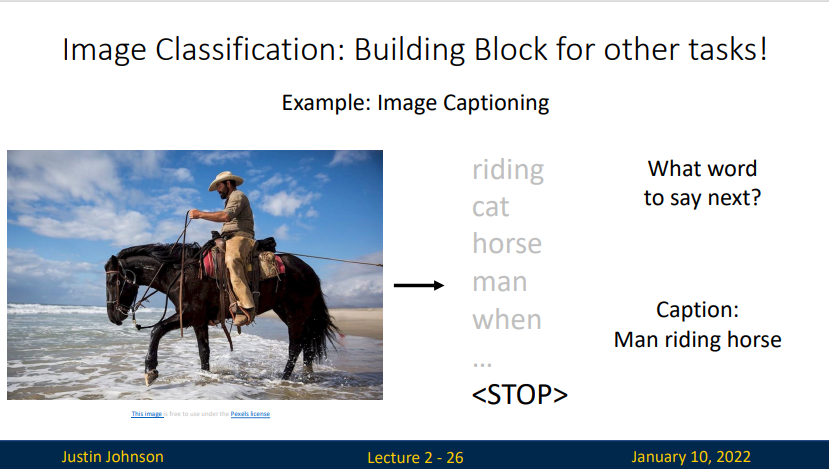
上面的图像识别出相关信息:背景、人、马等等,通过程序处理可以得到一份图像解释(Image Captioning):人骑着马。
An Image Classifier
no obvious way to hard-code the algorithm for recognizing a cat, or other classes.
Machine Learning: Data-Driven Approach
- Collect a dataset of images and labels
- Use Machine Learning to train a classier
- Evaluate the classifier on new images.
| Python | |
|---|---|
First classifier: Nearest Neighbor
- Train: Memorize all data and labeles
- Predict: Predict the label of the most similar training image
这个分类器和卷积神经网络没有任何关系,实际中也极少使用而且其非常简单,但通过实现它,可以让读者对于解决图像分类问题的方法有个基本的认识,也就是机器学习系统的两个基本部分——训练、预测。
Nearest Neighbor 算法将测试集中的数据与训练集中的数据进行比较,然后将它认为最相似的训练数据的标签赋给测试集中的数据。
Distance Metric to compare images
Nearest Neighbor Decision Boundaries Decision boundary is the between two classfication regions which can be noisy as it is affected by outliers.
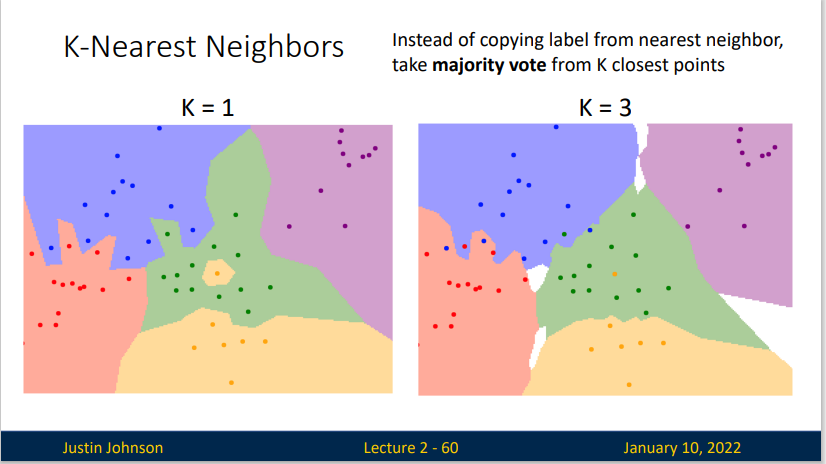
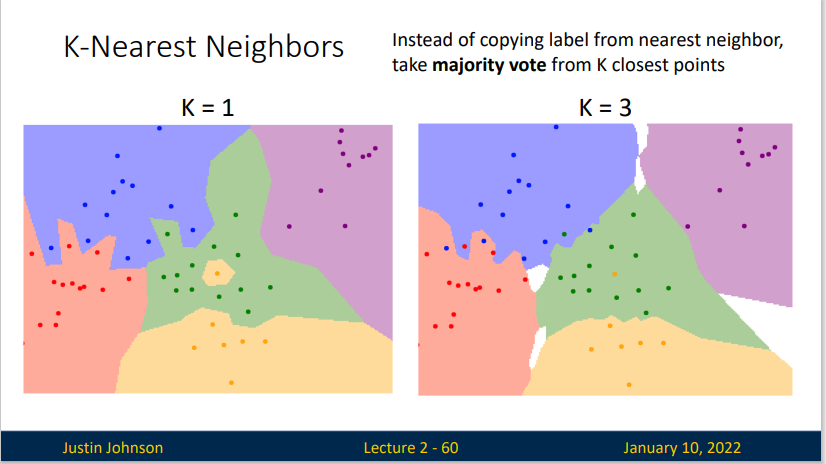
K-Nearest Neighbor
如果只是将最相似的那一份训练数据的标签来做为测试数据的标签,这不是很奇怪嘛?因为这意味着,如果这一份测试数据的一些特点恰巧和训练数据的特点相似,那不管这份数据实际上是什么,他往往会被赋予训练数据的标签。这是独裁者的做法。比如说我们由一只青蛙和一只猫,这两个生物的外表颜色很相近,且站位也相似,那么这只猫很有可能会被识别成一只青蛙。
我们会希望提高识别的准确性,因此,与其找一份最相似的数据标签,为什么不多用几份呢?这就是K-Nearest Neighbor算法。更高的K值可以让分类的效果更平滑,使得分类器对于异常值更有抵抗力。
(简单概括:民主比独裁好)
For K-Nearest Neighbors, Distance Metric
With the right choice of distance metric, we can apply K-Nearest Neighbor to any type of data!
As the number of training samples goes to infinity, nearest neighbor can represent any function
Hyperparameters
在机器学习中,超参数(hyperparameters)是事先给定,用来控制学习过程的参数。
超参数可分为模型超参数(Model Hyperparameters)和算法超参数(Algoriithm Hyperparameters)。模型超参数主要用于模型选择,其无助于学习训练集特征其无助于学习训练集特征;而算法超参数理论上对模型的性能没有影响,而会影响学习的速度和质量。一个典型的模型超参数是神经网络的拓扑结构及大小;而学习率和批量大小(Batch size)、小批量大小(Mini-Batch size)则是典型的算法超参数。
设置超参数:
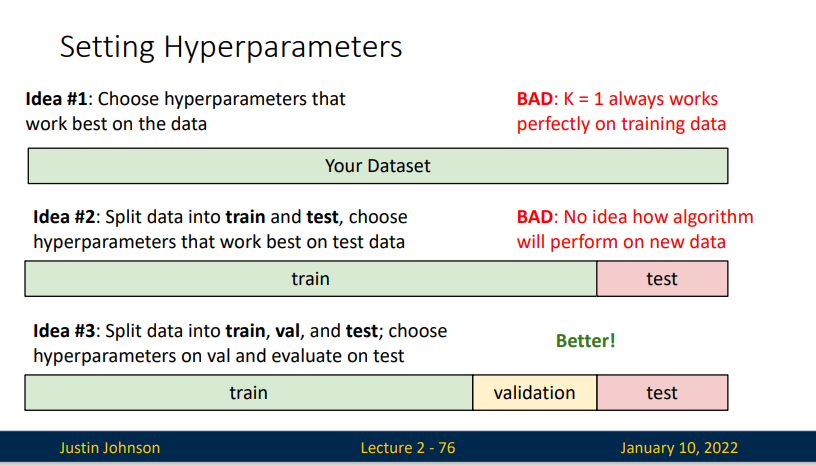
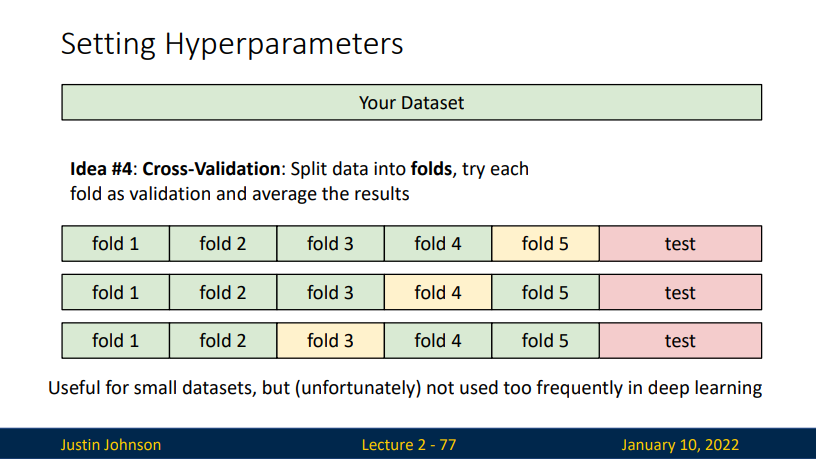
对于一份数据集,我们该如何划分这类数据集 - 直接选择在数据集上拟合效果最好的超参数 缺点: 效果最好的时候是 K=1(但这并不是我们想要的效果) - 将数据集划分成训练集和测试集,选择在测试集上拟合效果最好的超参数(留出法) 缺点:如果我们有一份新数据集的话,我们并不知道我们效果如何 - 将数据集划分成训练集、验证集和测试集,选择在验证集上拟合效果最好的超参数,并在测试集上评估。 - 将训练集分成K折,然后将每一折作为验证集,取均值。(又称K折交叉验证集) - 在小数据集上很有效,但是在深度学习中不常用。
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nearest Neighbor Classier
Problem: Curse of Dimensionality (维数灾难)
For uniform converage of space, number of training points needed grows exponentially with dimension.
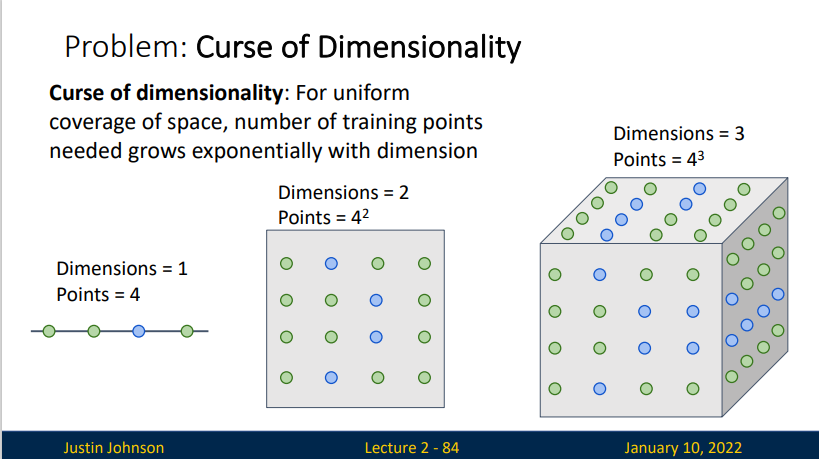
举例来说,100个平均分布的点能把一个单位区间以每个点距离不超过0.01采样;而当维度增加到10后,如果以相邻点距离不超过0.01小方格采样一单位超正方体,则需要\(10^{20}\) 个采样点:所以,这个10维的超正方体也可以说是比单位区间大\(10^{18}\)倍。于是带来问题时,随着维数的提高,可用的数据变得很稀疏。因此平常使用的数据组织策略就会变得极其低效。
Nearest Neighbor分类器在某些特定情况(比如数据维度较低)下,可能是不错的选择。但是在实际的图像分类工作中,很少使用。因为图像都是高维度数据(他们通常包含很多像素),而高维度向量之间的距离通常是反直觉的。
K-Nearest Neighbor on raw pixels is seldom used
- Very slow at test time (K=1 O(N))
- DIstance metrics on pixels are not informative
Nearest Neighbor with ConvNet features works well!
Summary
- In Image classification we start with a training set of images and labels, and must predict labels on the test set
- Image classification is challenging due to the semantic gap: we need invariance to occlusion, deformation, lighting, intraclass variation, etc Image classification is a building block for other vision tasks
- The K-Nearest Neighbors classifier predicts labels based on nearest training examples
- Distance metric and K are hyperparameters
- Choose hyperparameters using the validation set; only run on the test set once at the very end!